Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
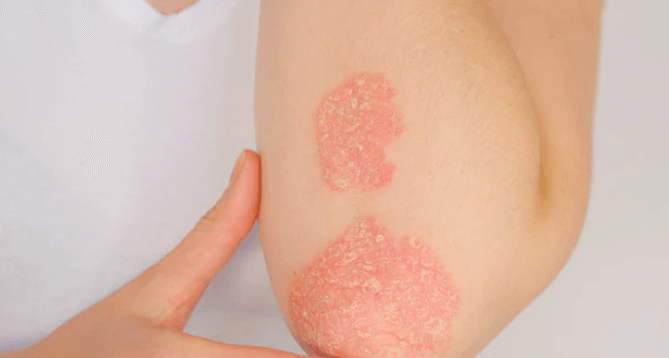
Psoriasis is a chronic (long lasting) disease that affects the skin. With psoriasis, skin cells build up rapidly on the surface of the skin, forming thick silvery scales and itchy, dry, red patches that are sometimes painful. It is an autoimmune disorder with no cure but treatments that help with symptoms. To manage the problem effectively, it’s important to understand what causes it, its symptoms and treatment options. Read the article to know all about psoriasis.
Causes of Psoriasis
Although the exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, scientists think a combination of genetic and environmental influences plays a role. Psoriasis is caused by an immune malfunction, where immune cells go into an ‘overdrive’ leading to their attack of healthy skin cells followed by a fast growth cycle.
Common triggers that can lead to or exacerbate psoriasis include:
- Genetics: It turns out that family history is important: If you have someone in your family who has psoriasis, you are more likely to get it, too.
- Stress: Stress can have a negative effect on your immune system and can cause flare ups.
- Infections: Symptoms can be brought about or made worse by certain infections, such as strep throat.
- Injury to Skin: A psoriasis outbreak can be caused by cuts, scrapes, or sunburn. You should talk to your dermatologist in Karachi and get treatment once symptoms appear.
- Medications: Psoriasis can be triggered by some drugs, such as lithium and some beta blockers.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Psoriasis symptoms can range from mild to severe depending on who has the disease. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Red patches of skin: Silvery white scales may often cover areas of the head, including the scalp, elbows, knees and lower back.
- Itching and burning: The affected areas may be itchy or cause a burning sensation.
- Dry, cracked skin: The skin can crack and bleed, it’s also very painful.
- Thickened nails: Nails can be affected by psoriasis and appear pitted, discolored, or crumble.
- Joint pain: In some people, psoriasis also plays a part in a type of arthritis — psoriatic arthritis — which causes the joints to be swollen and painful.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several different types of psoriasis, including:
- Plaque psoriasis: Thick, red patches of skin – the most common type.
- Guttate psoriasis: This form often is triggered by infections and presents itself as small, drop shaped lesions.
- Inverse psoriasis: It affects folds of skin, e.g. armpits or groin, and is usually red and shiny.
- Pustular psoriasis: It causes pus filled blisters on the hands and feet.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis: It is a severe form which causes generalized and widespread redness and scaling all over the body.
Psoriasis Treatment Options
There is no cure for psoriasis but treatments that keep the symptoms in check and prevent flares are possible. Treatment options include:
Topical Treatments
- Corticosteroids: The creams commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow skin cell production.Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Vitamin D analogs: Vitamin D in synthetic forms slows the growth of skin cells.
- Retinoids: In addition, these vitamin A derivatives help control the normal production of skin cells.
- Salicylic acid: This removes dead skin and scaling along with related impurities.
- UVB light therapy: Ultraviolet light exposure of the skin can slow the growth of skin cells.
- PUVA therapy: It combines UVA light exposure with a drug called psoralen to sensitize the skin to the treatment.
Medications
For moderate to severe cases, doctors may prescribe medications that work throughout the entire body, including:
- Methotrexate: It suppresses the immune system in order to reduce inflammation.
- Biologics: Change of genus of psoriasis by targeting specific parts of the immune system that trigger psoriasis.
- Cyclosporine: A strong drug that prevents the immune system from overreacting but can create unwanted side effects.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis symptoms:
- Moisturize regularly: Dry scaling can be prevented by keeping the skin hydrated.
- Take soothing baths: Warm Soaking in warm water with Epsom salts or colloidal oatmeal will help relieve itching and inflammation.
- Manage stress: Yoga, meditation or deep breathing can help lower flare ups by stress management techniques.
- Maintain a healthy diet: In some cases, eating a well balanced diet and not eating foods that aggravate inflammation like processed foods may help.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a lifelong condition which needs to be kept in control. Unfortunately, there is no cure for this condition, but medical treatment aimed at minimizing flare up and different lifestyle interventions can help improve the quality of life for people who must live with this condition. If you think you have psoriasis, consult a dermatologist to talk about your options and determine a suitable treatment plan.